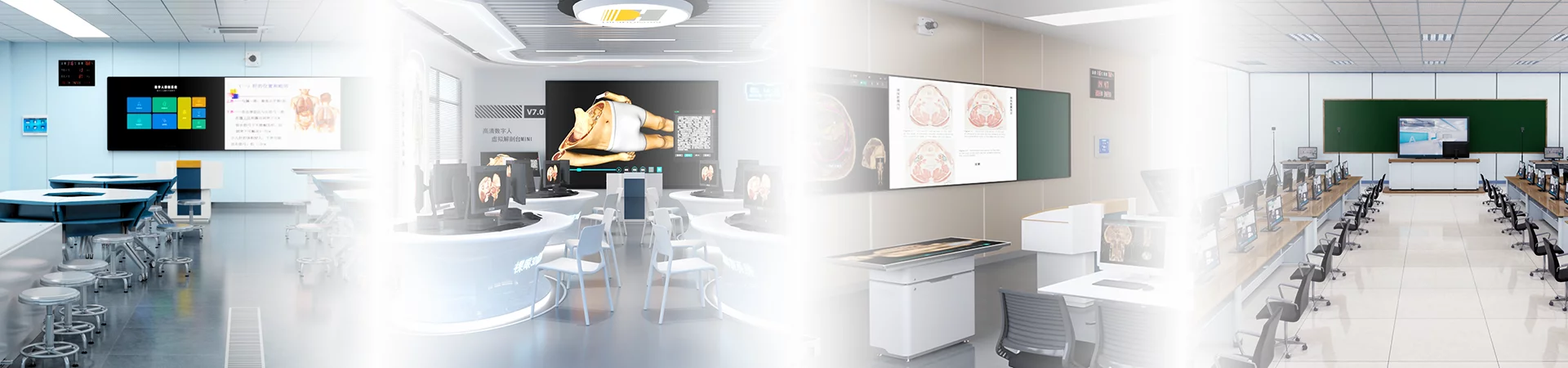
As a leading expert in the field of medical education, I am excited to discuss the latest industry trends and analysis surrounding anatomy laboratories. These state-of-the-art facilities have become essential for training future healthcare professionals, and their impact is particularly evident in North Carolina.
The Advancements in Anatomy Laboratory Facilities
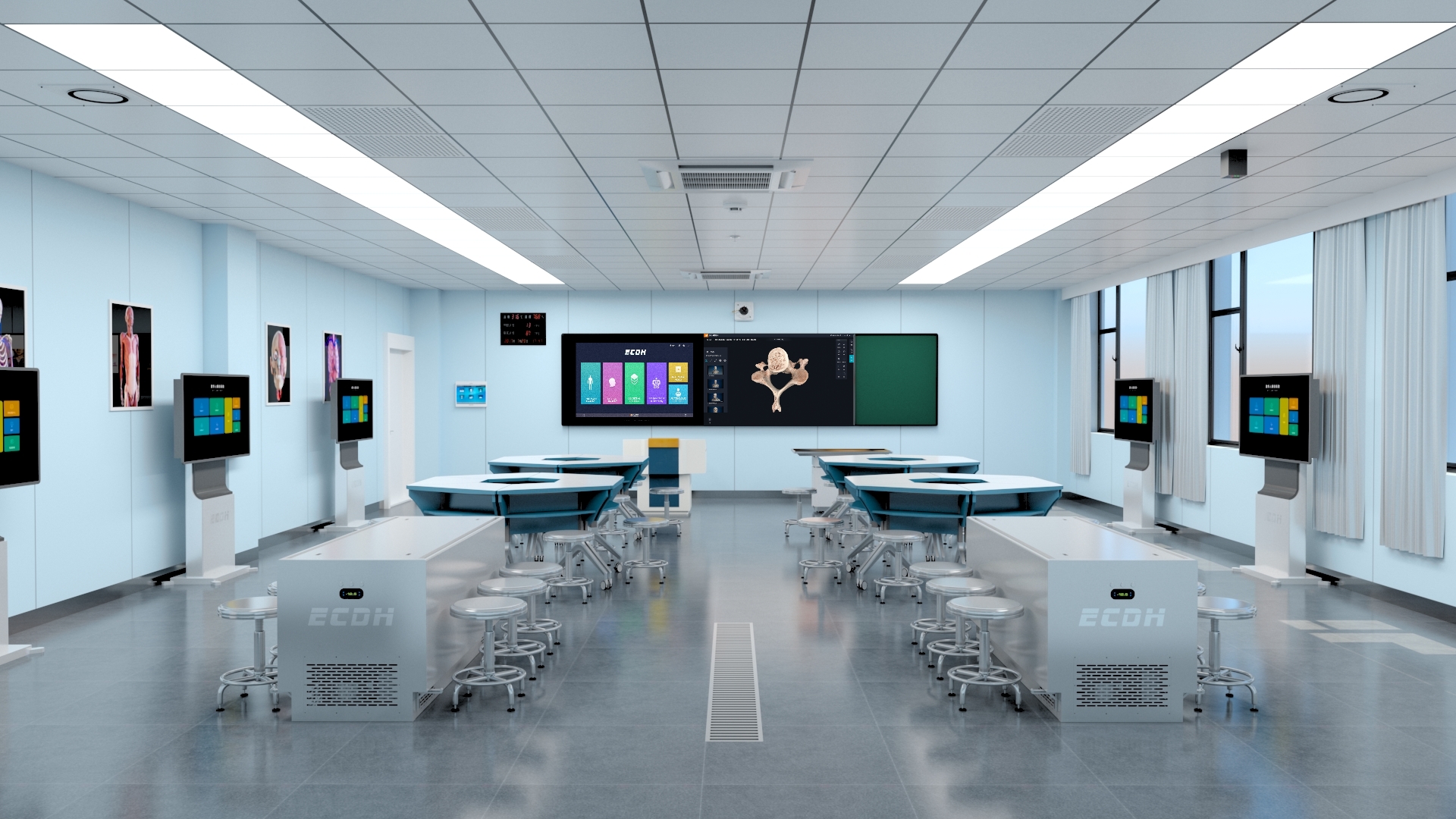
In recent years, anatomy laboratory facilities have undergone significant advancements to enhance the learning experience for students. The integration of cutting-edge technology has revolutionized traditional teaching methods by providing hands-on opportunities that were previously unimaginable.
One notable innovation is the introduction of DIGIHUMAN, a lifelike anatomical model that replicates human structures with remarkable accuracy. This advanced tool allows students to explore intricate details of the human body through interactive digital simulations, significantly improving their understanding and retention of anatomical knowledge.
The Role of DIGIHUMAN in Medical Education
DIGIHUMAN has emerged as an invaluable asset within anatomy laboratories across North Carolina. Its realistic representation enables students to study complex anatomical structures from various angles without relying solely on cadavers or textbooks. By interacting with this virtual model, learners can dissect different layers and systems at their own pace while receiving real-time feedback on their progress.
This innovative technology not only enhances student engagement but also promotes collaborative learning experiences. With DIGIHUMAN’s ability to be accessed remotely, educators can facilitate virtual group discussions where students from different locations can interact and learn together seamlessly.
Anatomy Virtual Dissection Table Software: A Game-Changer
Another noteworthy development within anatomy laboratories is the advent of anatomy virtual dissection table software. This software provides a simulated dissection experience using touch-sensitive screens integrated into specially designed tables.
By utilizing this software, students can virtually dissect cadavers and explore anatomical structures in a controlled environment. The interactive nature of the software allows for a more immersive learning experience, enabling learners to manipulate virtual organs and tissues with precision.
Furthermore, anatomy virtual dissection table software offers additional features such as 3D visualization, cross-sectional views, and access to comprehensive libraries of anatomical resources. These tools empower students to develop a deeper understanding of human anatomy while honing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Conclusion

The advancements in anatomy laboratory facilities have undoubtedly transformed medical education in North Carolina. Through the integration of DIGIHUMAN models and anatomy virtual dissection table software, students now have access to cutting-edge tools that enhance their learning experiences.
These innovations not only bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application but also foster collaboration among future healthcare professionals. As technology continues to evolve, it is evident that anatomy laboratories will remain at the forefront of medical education by providing an immersive and dynamic platform for aspiring doctors, nurses, and other healthcare practitioners.

